- Accounts
-
Shop
- Bundle / School Shop
- Personal Shop
-
SoundcheckPro
- Getting Started
-
Session Mode
- Console Selection
- Session Overview
- Source Type Selection
- Destination Tab
- Sources Tab , Audio Files
- Mixer Input, Speaker Output
- Save & Load Sessions
- Settings
- Console Operation
- Audio Effects
- Education
- Advanced Functions
- Troubleshoot
- Xena Mixer
- Yamuka Mixer
- Maggie Mixer
- Zedd Mixer
- DG32 Digital Mixer
- SteeV88
- Audyssey Console
- Xena Web App
- EDU Portal
- Virtual Studio XR
Mixer Input, Speaker Output
- Docs
- SoundcheckPro
- Session Mode
- Mixer Input, Speaker Output
Background
Now that we understand the environment we could start to use the mixer. Follow the common steps of signal flow to get sound to the speakers.
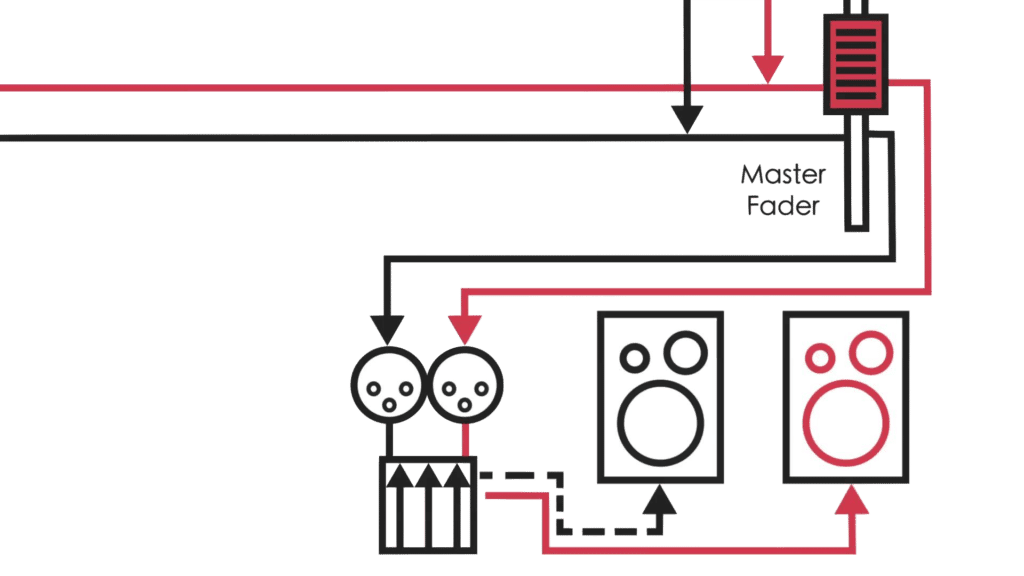
Steps
- Load Audio Files and Play
- Raise channel input gain . Observe meters for a healthy signal.
- Assign channel Main Output (Mix or L/R)
- Raise channel fader. Observe meters for healthy signal.
- Select main output on monitor control
- Slowly raise monitor gain.
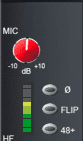
Input Gain
The entry point for incoming audio into the console. The level of signal is controlled by this parameter. Use the meters to achieve a healthy signal.
Main Output Bus
The output of channels are routed through a stereo bus to be sent to the speakers. Depending on the features of the console, more stereo bus destinations may be offered.
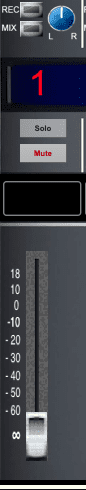
Channel Fader
Controls the level of signal being sent out of the channel.
Monitor Select
Assign which stereo bus is routed to the speakers.
Typical options:
- Main or L/R or Mix – Common to channelstrips
- Cue – Headphone mix
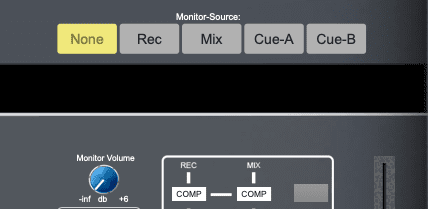
Monitor Gain
With the desired output bus selected, control the level of signal being sent to the speakers.
Conclusion
These are the common steps used to approach most recording consoles. Check back soon for additional details.